A tool function is an optional feature that can be utilized within the AI Assistant Template in m-Power.
The purpose of the tool function is to provide the AI Assistant template real-time information which can be utilized within the chat interactions, or even in behind-the-scenes workflow that the assistant is invoked from. Tool functions allows the developer to configure their AI Assistant application to interact with external data via any of the following options:
- Query live data on the licensed database via a retrieval application.
- Run external business logic via External Objects.
- Query information from an AI Content Retrieval (this document).
What is a Content Retriever?
A Content Retriever is an application you create in m-Power that lets you upload documents (like PDFs or plain text files) so your AI Assistant can use them as a knowledge base. Instead of relying only on the assistant’s general knowledge, you can provide it with very specific information — like your company handbook, employee policies, or product documentation.
When content is uploaded, m-Power doesn’t store or search the file like a normal database. Instead, it breaks the content into small, readable pieces called chunks. Each chunk is then converted into a special numeric format (a vector) that represents the meaning of the text. These vectors are stored in a vector database, which allows the system to quickly find chunks that are most similar to the user’s question. When someone asks a question, m-Power finds the closest-matching chunks and passes them to the AI model so it can craft an informed response. Want to learn more? See this gentle introduction to vector databases.
Think of it this way: If your AI Assistant is a helpful librarian, the content retriever is the special filing system that lets the librarian find the right page of the right book every time.
Why Use a Content Retriever?
A Content Retriever is ideal when you want your AI Assistant to reference large amounts of information that doesn’t change often. Instead of training or hardcoding answers, you can simply upload documents and let the assistant search through them when answering questions.
For example:
- Company policies — Upload your employee handbook so the assistant can answer HR-related questions.
- Product documentation — Give your assistant access to technical manuals, user guides, or troubleshooting steps.
- Training materials — Upload standard training documents to provide consistent answers to new hires.
However, if your information changes frequently—like inventory levels or daily accounting numbers—a Content Retriever may not be the right option. In those cases, it’s better to use an Application Tool Function that pull in real-time data instead.
Best Practices
To get the best results from your retrievers, keep these tips in mind:
- Use smaller documents. Instead of uploading a 100-page handbook, break it into separate documents based on topics such as “Vacation Policy”, “Health Insurance”, or “Code of Conduct.” This makes search results more accurate.
- Stick to text-based formats. Upload PDF, Markdown, or plain text files. If your document is in Word or HTML, convert it to text or Markdown first.
- Name documents clearly. Use descriptive file names like Vacation_Policy.pdf or Product_ABC_UserGuide.pdf so it’s easy to recognize them later.
- Keep content up to date. If policies or documentation change, reupload the updated version and remove older ones to avoid outdated answers.
Content Retriever App Properties
When building a Content Retriever in m-Power, you don’t need to define a data model or define tables like you would with most templates. Instead, you simply build the retriever, upload your content, and m-Power handles how the content is stored and accessed.
However, you can customize how m-Power breaks your documents into smaller pieces (called chunks) and how those chunks are processed using the properties below. These settings affect accuracy, search quality, and how your AI Assistant interprets your content.
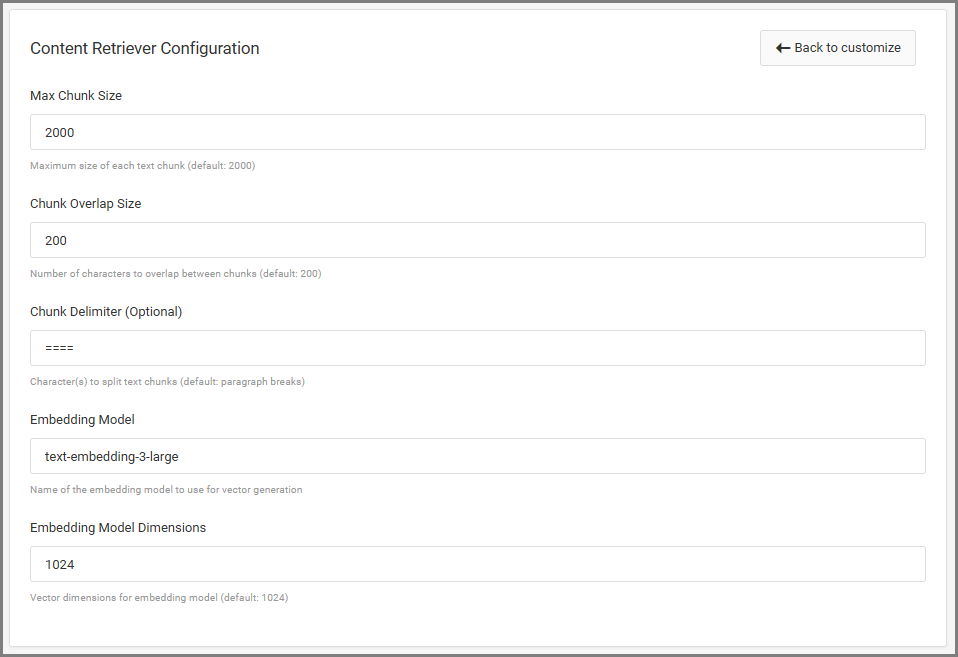
Max Chunk Size
The maximum number of characters allowed in each chunk of text.
- A larger chunk size means fewer, longer pieces of content are created. This gives the AI more context at once but may include extra or unrelated information.
- A smaller chunk size creates more, smaller chunks. This makes answers more focused but may lose surrounding context.
- The default value (2000) works well for most situations. Only lower it if the AI is giving unclear or overly broad answers.
Chunk Overlap Size
Controls how many characters are shared between one chunk and the next.
- Overlapping ensures that important sentences aren’t cut in half between chunks.
- If your content flows naturally between sections (like paragraphs in a policy), you may want more overlap so the full idea isn’t lost.
- If your document contains unrelated sections (like FAQ lists or unrelated topics), you can reduce the overlap to avoid pulling in unrelated information.
Chunk Delimiter (Optional)
Defines what m-Power should use to split your document into chunks.
- Default: Paragraph breaks
- If you can edit your document before uploading, you can control where chunks begin and end by using a specific symbol or text pattern.
- You can set this to characters like ====, —, ###, or any custom marker that separates sections clearly.
Embedding Model
The AI model used to convert each chunk into a numeric vector for searching.
Default: text-embedding-3-large
Embedding Model Dimensions
The size (number of values) in each vector created by the embedding model.
Default: 1024
Tuning Guidance
These settings don’t change how the Content Retriever looks to users, but they do impact how well the AI can find and understand the right information. Here’s when you might want to adjust them:
- Increase Max Chunk Size if the AI is missing context or only giving partial answers.
Example: Your PTO policy spans several paragraphs, but the assistant only references one sentence and misses the full explanation. A larger chunk size helps the AI see full ideas at once. - Decrease Max Chunk Size if answers feel too broad or include unrelated details.
Example: You uploaded a long product manual, and when someone asks about warranty information, the AI also talks about installation steps because they were part of the same large chunk. A smaller chunk size helps the AI focus on just the relevant section. - Increase Chunk Overlap Size when ideas flow across paragraphs and shouldn’t be separated.
Example: A policy document explains eligibility in one paragraph and exceptions in the next. More overlap ensures both parts are considered together when answering a question. - Decrease Chunk Overlap Size when sections are unrelated and shouldn’t influence each other.
Example: A document that lists separate FAQs or policies where each section stands alone. Less overlap prevents the AI from pulling in information from the previous or next section.
Uploading a Knowledgebase
You’ll typically upload a separate document for each topic you want your AI Assistant to reference—for example, one for company policies and another for product documentation.
When you run your Content Retriever application, you’ll see:
- Upload Box: Drag and drop files here, or click to browse your computer.
- Uploaded Documents List: Shows the filename, upload date and time, file size, and chunk size. You can reupload or delete any document you no longer need—doing so removes it from the knowledgebase.
- Summary Panel: Displays the total number of uploaded files and the combined chunk size.
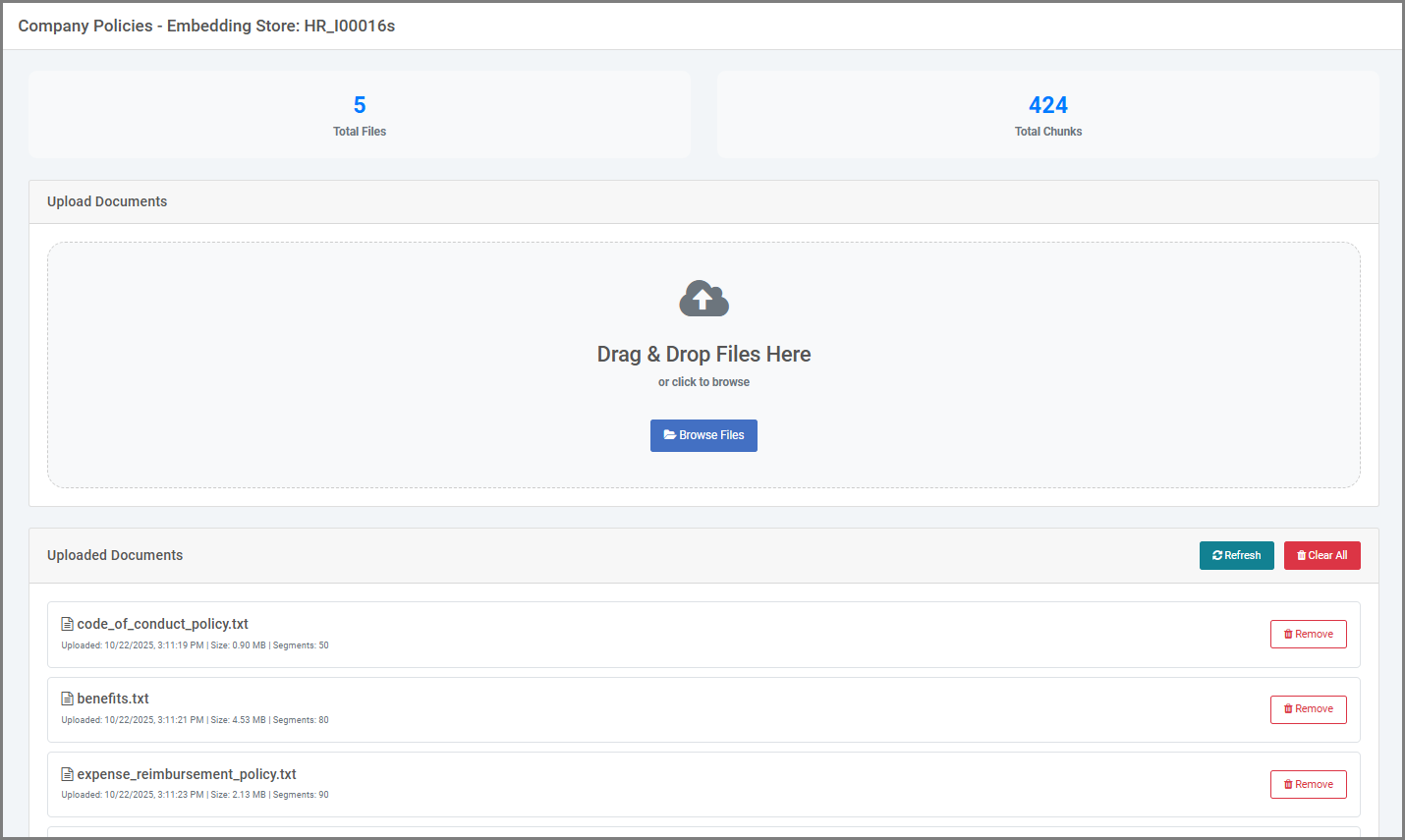
To upload a document:
- Prepare your file: Use text-based formats such as PDF, plain text, or Markdown. If your document is in Word, HTML, or another format, convert it to Markdown using a free online tool. Learn more about Markdown here.
- Upload your file: Drag it into the upload box or select it from your computer.
- Processing: Once uploaded, m-Power breaks the file into chunks, converts them into vectors, and stores them in the vector database. The processed chunks will then appear in your Uploaded Documents list.
Connect a Content Retriever to Your AI Assistant
Uploading documents is only the first step. To allow your AI Assistant to use this content in conversations, you need to add the Content Retriever as a Tool Function in your AI Assistant application.
In the AI Assistant’s App Properties, open the Tool Functions tab and create a new tool. Select Content Retriever and choose the retriever application you previously built. This links the assistant to your stored knowledge so it can search your documents when answering user questions.
Content Retriever Tool Function Configuration
After linking, you can configure how your assistant uses the Content Retriever:
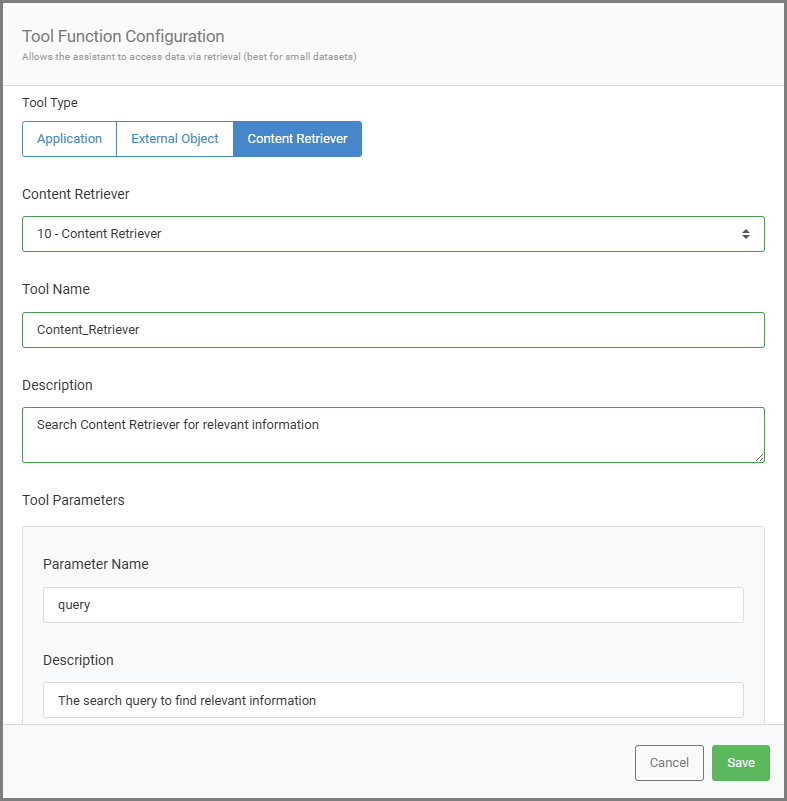
Tool Name: The name that is used when a prompt is sent to the LLM. This name can also be specifically referenced in the System Prompt of the AI Assistant. Spaces in the name will be replaced with underscores for LLM compatibility (e.g., company_PTO_policy).
Description: A short, clear description of the retriever’s purpose to help the AI understand when to use it (e.g., Provides answers about company Paid Time Off policies).
Tool Parameter Name: Set to ‘query’ by default. You can customize this to match the type of information the retriever searches (e.g, Use ‘PTO_policy’ instead of the default ‘query’).
Tool Description: The default is “The search query to find relevant information.” You can make this more specific to guide the AI (e.g., Searches for information about company Paid Time Off policies).
Once saved, your AI Assistant can search your uploaded documents and deliver responses based on your company’s content—not just general AI knowledge.
