A tool function is an optional feature that can be utilized within the AI Assistant Template in m-Power.
The purpose of the tool function is to provide the AI Assistant template real-time information which can be utilized within the chat interactions, or even in behind-the-scenes workflow that the assistant is invoked from. Tool functions allows the developer to configure their AI Assistant application to interact with external data via any of the following options:
- Query live data on the licensed database via a retrieval application (this document)
- Run external business logic via External Objects
- Query information from an AI Content Retrieval
How to use a Tool Function?
To access the tool functions within your AI Assistant, navigate to:
3. Customize -> Edit Properties -> ‘Tool Functions’ tab:
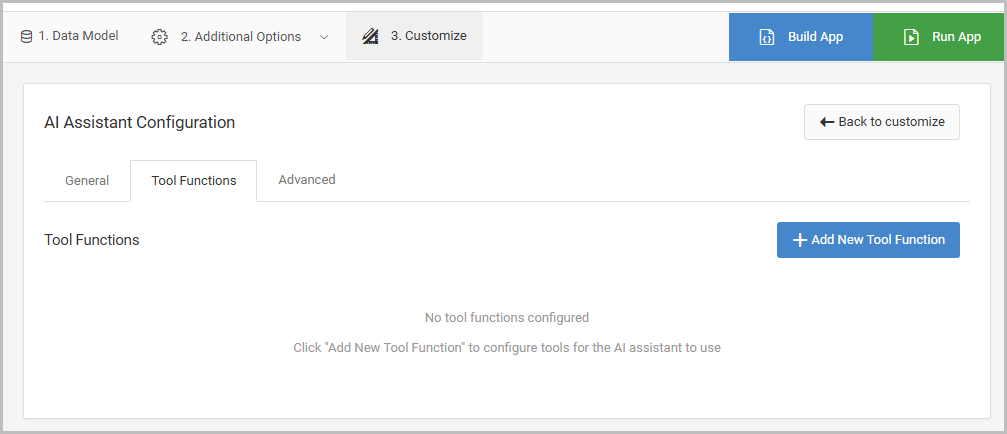
Why use a Tool Function?
As is often the case with AI tools, there is no one-way to utilize AI. The use case will depend entirely on your chatbot’s purpose. Here’s a few examples that can help explain where tool functions come into play:
Example 1: You have an AI Assistant that serves a chat for end-users to add items on the screen to their cart. To add an item to a cart, the item’s stock quantity must be queried in real-time. Building a separate Multiple Row retrieval over the products and their quantities allows the assistant to correctly determine if a product is in stock, prior to adding it to the user’s cart.
Example 2: You have a helpdesk ticketing system where submitted tickets are automatically assigned to the person with the fewest open tickets in their queue. When a new ticket is submitted, an AI Assistant queries a Multiple Row retrieval that returns the existing tickets for each helpdesk staff individual. The assistant queries this list and finds the individual with the lowest number of open tickets. Once found, the appropriate staff can be assigned to the ticket by the same workflow updating the database record.
Example 3: Users interact with an AI Assistant as a chatbot in an m-Power application that shows a list of recently placed orders. A user can inquire to the AI Assistant about a customer (via a Single Row retrieval), and the assistant can query the customer data to return appropriately details about the inquired customer.
Walkthrough
In this documentation, we’ll follow Example 3 from the above section.
I’ve created an AI Assistant called “Orders”, whose purpose is to provide my end-user with a chat bot that will be interacted directly by the end-user (via chat) and will need to utilize my live data to answer questions about placed orders, customer information, and product inventory on hand.
I’ve implemented my chat bot into a retrieval that displays all customer orders on the screen.
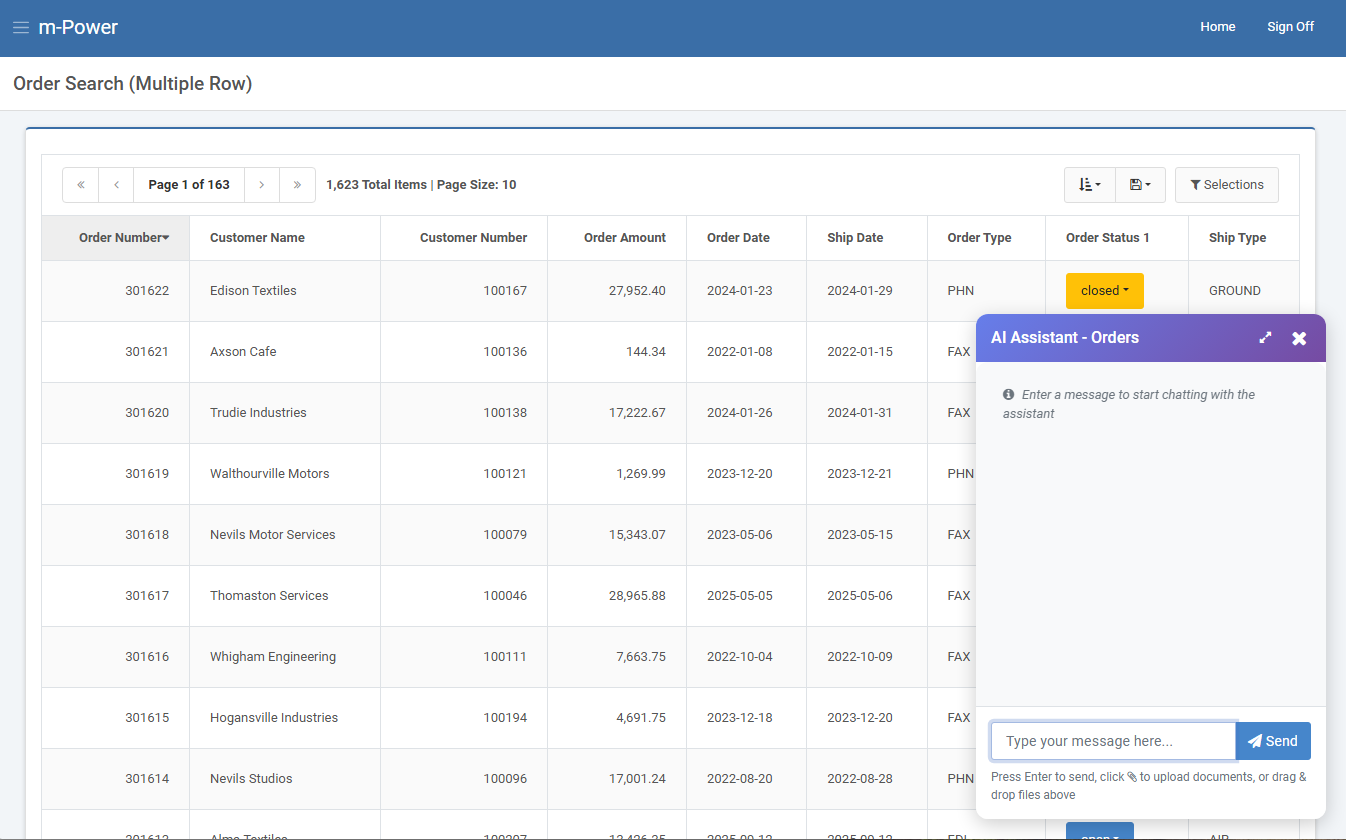
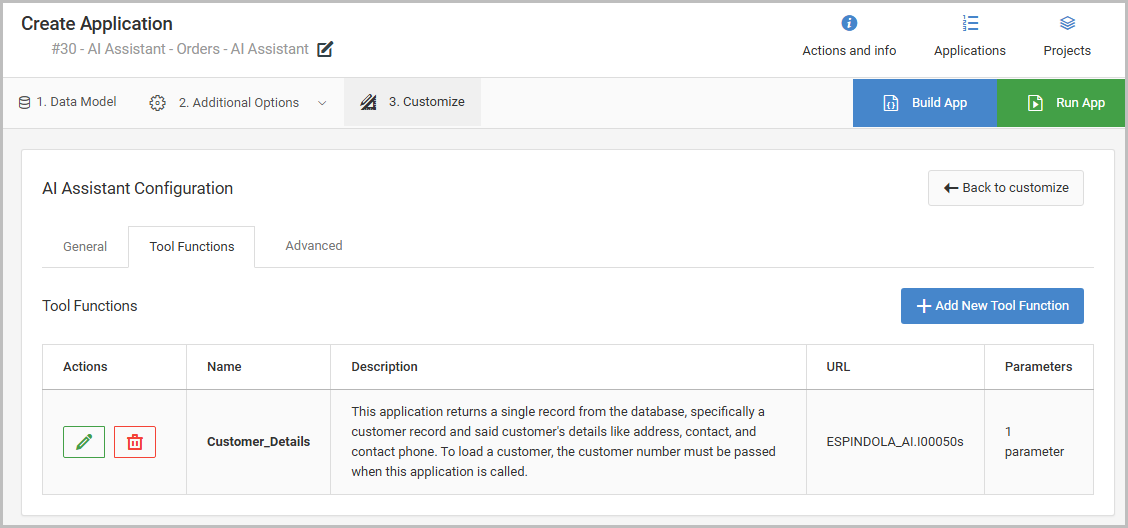
A Single Row retrieval called ‘Customer Details’ has been built over my customer master table, and that will be utilized as a tool function in the AI Assistant application. By adding this as a tool function, the chat bot can query my customer information in real-time and provide meaningful information about customers as a user inquires about them.
1. Configuration
To add my tool function, I’ll select the ‘Add New Tool Function’ option below:
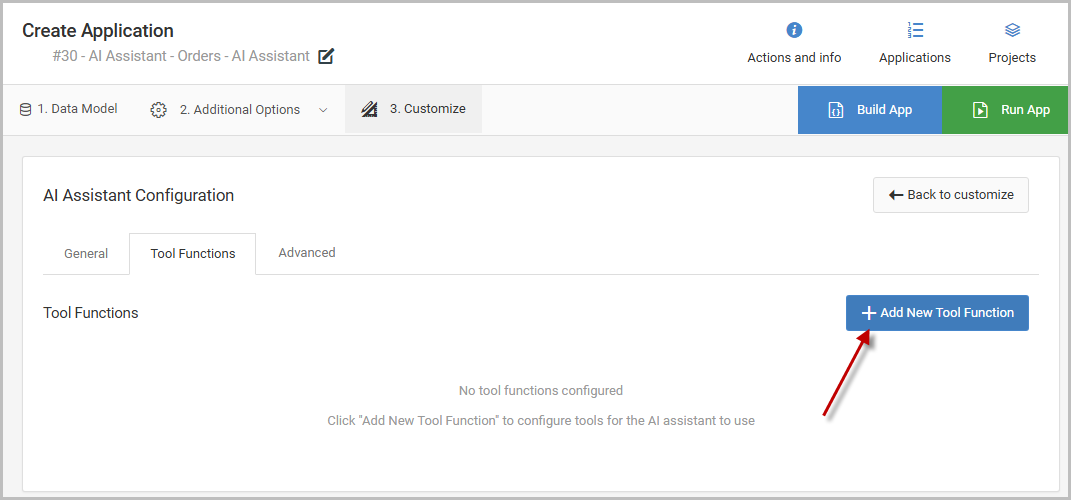
The following modal to configure the tool function will appear, where I will select Application as the tool type, as shown in Figure 4.
When using “Application” as the tool type, either a Multiple Row or Single Row Data List template must be utilized. In this example, my single row retrieval, Customer Details, will be selected and configured.
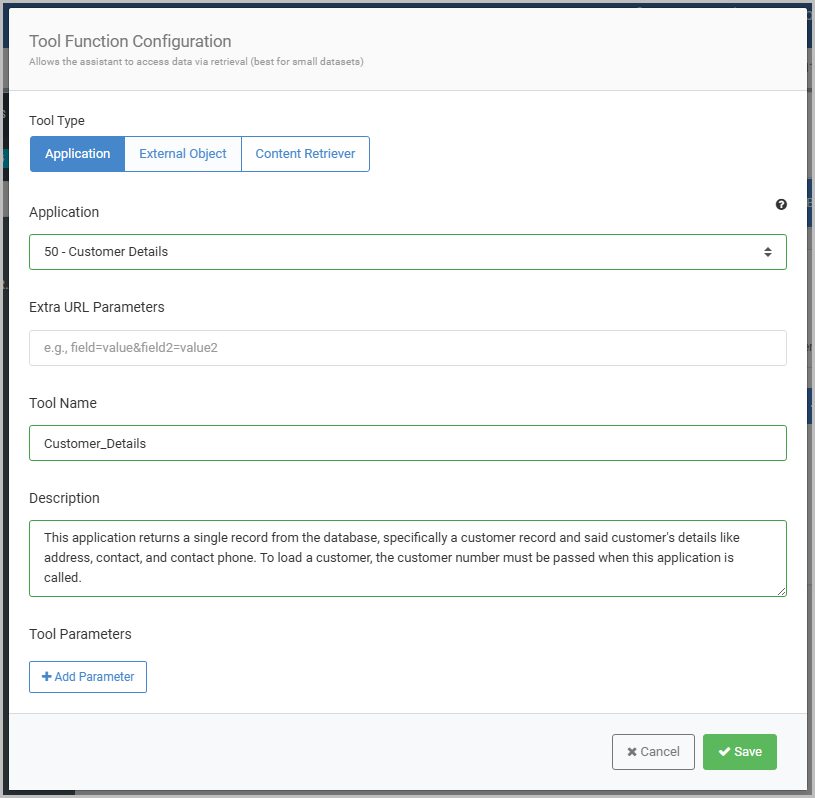
As will often be the case, a tool function will need information passed in at runtime from the AI Assistant in order to query the right information at runtime.
Selecting the “+ Add Parameter” button will expand the Tool Parameters sections, where the necessary parameters can be defined, allowing the AI Assistant to pass values from the inputted message to the retrieval application I’ve selected.
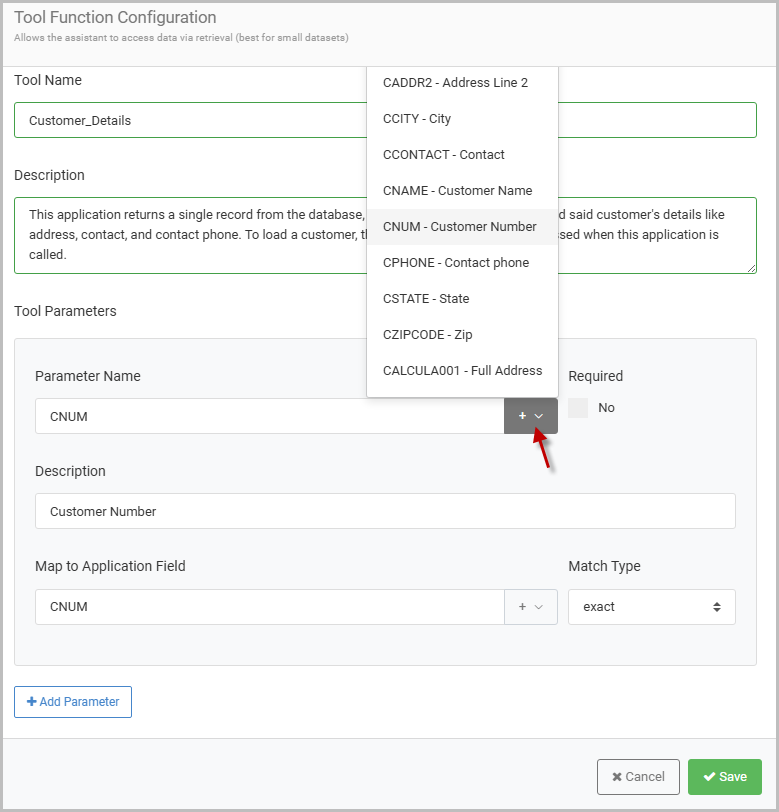
When selecting a retrieval to be the source of the tool function, utilize the pulldown shown in Figure 5 to select the field from retrieval’s data model that the AI Assistant will pass a value directly into.
In this situation, the customer details retrieval will need to be passed a customer number to know which customer to search for, meaning that parameter must be mapped accordingly.
Take note of the “Exact Match” option as well. In this case, choosing exact will mean the parameter value is looked for exactly as-entered. In other situations where a character parameter is being defined, the other option of search will mean the parameter value is looked up via a contains relationship.
After saving the tool function, the following information can be reviewed immediately for accuracy as show in Figure 6.
2. Edit the System Prompt
In the system prompt of my AI Assistant, the following guidelines have been provided, which as seen below provides additional context about the Customer_Details tool function defined back in the data model.
#NOTES
1. The user can ask about a specific customer details by supply the customer number, in a numeric format of ######. For example, a customer number is 100001, 100002, 100003, etc. Use the "Customer_Details" tool function and pass the customer number to it.
The user MUST supply a customer number prior to you returning information from the "Customer_Details" tool function. Return the information in a bullet point list. Adding this information to the system prompt should be considered supplemental information – as recall the description provided when configuring the tool function earlier will be passed to the LLM and provide the most immediate instruction as to what the tool function is utilized for. Learn more about writing a System Prompt here.
3. Runtime
At runtime, I can interact with the AI Assistant chat bot and test out my tool function call to the customer details retrieval.
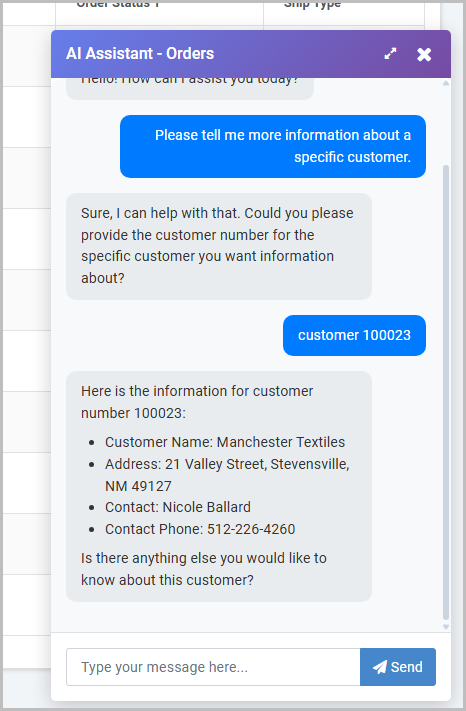
Notice a customer number has been indicated in the tool function configuration and the system prompt as required, so the AI Assistant will appropriately ensure that this information is passed before any information is returned.
