This document will cover a high-level description of how to add Artificial Intelligence (AI) into your m-Power application. Specifically, this document will guide developers on how to enable AI, link out to more m-Power documentation on specific AI topics, as well as cover frequently asked questions.
Introduction
m-Power allows you to include AI in a number of ways into m-Power including:
- Chatbot
- Reading input from a maintainer (for AI workflow integration)
- Uploading a knowledge base
- Accessing a custom knowledgebase (via a Content Retriever)
- Upload and Parse a Document (in development)
- Outputting a document from AI response (in development)
No matter what approach you try, the methodology is similar: Information from the user (what they entered) plus information you’ve provided (a system prompt) is sent to a Large Language Model provider of your choice, and information is then returned. This information can come in the form of a response in a chatbot, but it could also be returned in the form of a JSON response which can then be read by an m-Power workflow, triggering further action (write to database, send an email, conditional actions, etc).
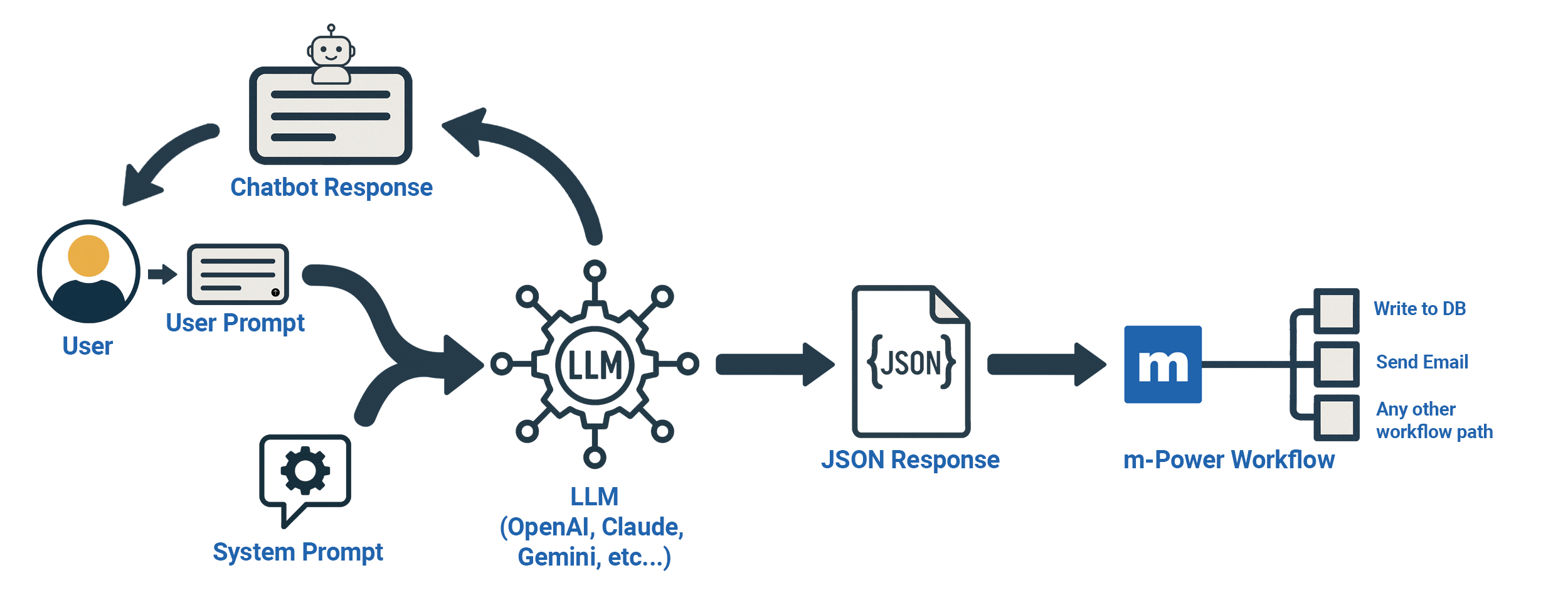
Setup
To configure AI, a few pre-requisites are required:
- Take the Q4 2025 m-Power update
- Sign up with an AI provider (Such as Open AI, Azure AI, Google Gemini, or Anthropic AI) and obtain an API key.
- Add the following properties to your /m-power/mrcjava/WEB-INF/classes/mrc-runtime.properties file:
enable_ai=true
enable_llm_logging=true
#Microsoft Azure config
azure_openai_api_key=
azure_openai_url=
#Anthropic config
anthropic_api_key=
#OpenAI config
openai_api_key=
#Google Gemini config
gemini_api_key=
#IBM Watson config
watsonx_api_key=
watonx_project_id=
#Groq config
groq_api_key=
groq_endpoint=Note: Depending on which of the 4 AI providers you are using, only fill out that entry and ignore the other providers.
Once completed, restart Tomcat
How do I obtain an API key?
API keys are typically created and managed within your organization’s account with your chosen AI provider (for example, OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Google Gemini, etc.). Because this involves your own security, billing, and access controls, the process of setting up the account and generating the key should be handled by whoever manages external services or cloud subscriptions at your organization (for example, IT staff, a system administrator, or an account owner). For this reason, our documentation does not include provider-specific, step-by-step instructions for obtaining API keys.
Building your first AI App – AI Assistant
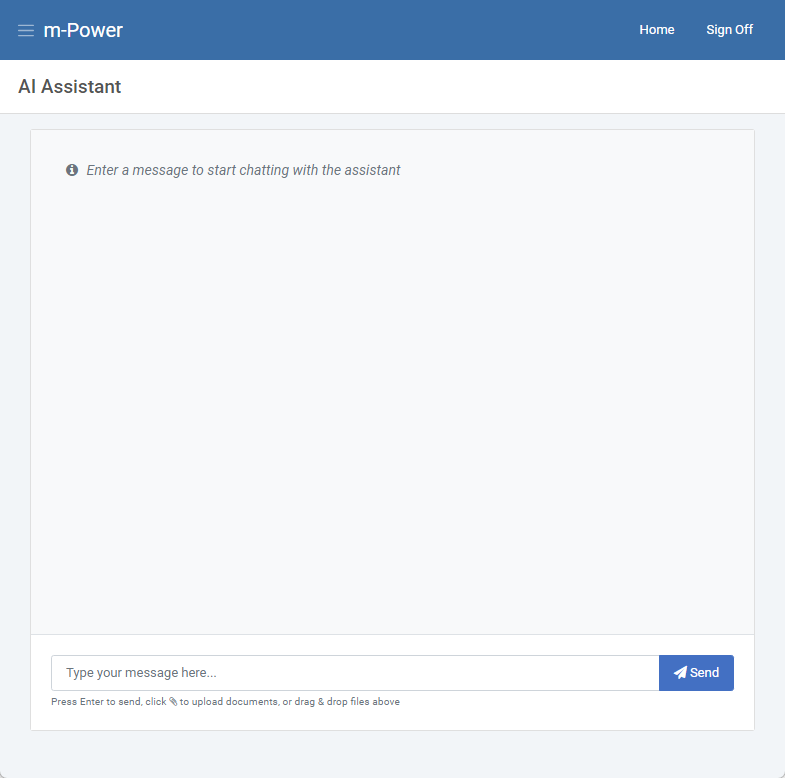
Go to the retrievals area, and build a new application. Select the “AI Assistant” template. This template doesn’t require you to choose a table or fields or even dimensions. Once you’ve done this click Build App.
Running the app will bring up a chat box which has the base knowledge of your selected AI provider and default model.
Making your AI Smarter
There are a few ways you can make your AI Assistant smarter:
Tool Functions – Application
Tool function – Applications are a way your AI can reference live database values to help better answer your user. Example: “AI ~ Can you show me a list of clients who have submitted an order within the last 30 days?” By linking a multiple row retrieval to your AI it can use this information as part of its knowledge. This is ideal for situations when the data you are accessing changes frequently. More information about Tool Function Applications here.
Tool Functions – Content Retrievers
Content retrievers are a way to create document repositories (knowledgebases) that can be referenced by the AI Assistant. Imagine you are building an AI Assistant to help employees understand various corporate policies. A content retriever would allow you to upload documented corporate policies to create a knowledge base. When employees interact with the assistant it will refer to information from the knowledge base applicable to the question or conversation. Content retrievers are a great solution for accessing data that is more stagnant. More information about building Content Retrievers and linking them to your AI Assistant here.
Tool Functions – External Objects
In the event you want to trigger an external object each time the AI is triggered, you can utilize this tool function.
System Prompts
System prompts are how you define the Assistant’s purpose and instruct it on how it should behave. You can help guide the AI to tell them what to expect, what to do, what not to do, and generally how to function. System Prompts are absolutely vital to a successful AI implementation. Simply put, the better a system prompt is written, the more accurate the AI will deliver your results. More information about writing System Prompts here.
Embedding your AI chatbot on another m-Power page
AI Assistants don’t have to be run stand alone. See this documentation to learn how to embed the assistant into any other m-Power application:
(How-To) Embed an AI Assistant in another m-Power application
AI Assistant Properties
General
Model — Each AI provider offers a variety of Large Language Models (LLMs). The usage price varies for each one, as does it’s overall specific function. Select the LLM that best fits for your specific need here.
Chat History Mode — Controls if you want AI to remember your chat just while the chat bot is open on the page or to retain it throughout the whole session.
Hide JSON from Chat Responses — Useful if you return JSON responses back from AI and want them to be hidden to the end user. More information about this here.
Tool Functions
Specify the m-Power applications or external objects that AI can reference to access supplemental information used to augment data from your environment.
Advanced
Max chat history messages — When chatting with an AI bot, old results are set to the LLM to help continuity of the conversation. Lowering this value may cause older parts of the conversation to be omitted whereas raising this number too much can confuse the AI.
Temperature — This value controls how precise the answer is. A lower value (.1 – .3) is good for factual responses. Where a higher value (.8+) is better for responses that require more creativity.
Max Tokens — AI providers charge you based on token usage (both input and output tokens). This value limits the LLM from responding above the specified amount.
Max Content Retriever Results — When a content retriever is accessed, this value tells the AI how many rows it should access based on proximity to what it thinks is a relevant answer. Lowering this number might cause the AI to miss valid resources. Raising this number may cause the AI to be confused with too much information. If the results seem to miss important context or can’t fully answer a question, try increasing the max retriever results slightly.
Content Retriever Min Score — This setting determines how closely a piece of content must match the user’s question before it’s included in the results. A higher value means the retriever will only include the most relevant information. A lower value allows broader results, which can sometimes include less-relevant content. If your retriever sometimes includes off-topic or inaccurate information, try raising the minimum confidence score
Incorporating AI within maintainer workflows
AI excels at the generation and analysis of text. With maintainer workflows plus AI you can perform actions that take advantage of both of these capabilities. First, you can pass information/text entered into any m-Power maintainer to AI for analysis, be it for sentiment analysis (ex: has the user submitted a critical or low priority issue?), categorization (which category does this user request fall into A, B or C?), and more. Next, to capitalize on text generation capabilities, you might have the LLM (Large Language Model) re-word the input from the maintainer, clean it up in some way, or even translate it to another language. Or, based on the Assistant’s knowledge base and system prompt, you may have it write an email or generate some other summary or response given the input text from the maintainer and then write it back to a database.
Given that workflow has many action types and the ability to conditionally execute these actions, you can create complex decision trees not just based on information from maintainer web forms and database lookups, but also AI assistant responses. For example, take information entered into a maintainer by a user and send it to an AI Assistant for categorization. If it returns category A then write something to DB, if it returns category B, write something else to DB, and if it returns category C send an email back to the user thanking them for submitting their request.
Document Parsing
Documents like PDFs and other text documents can be uploaded to an AI Assistant. You can instruct the assistant to parse and extract pieces of the document that can then be integrated into workflows to write the data, send emails, etc. A simple example would be to upload an invoice, extract basic information like name, $ amount, PO# etc, and then write that to a database. More information about that can be found here soon (in development).
Document Creation
Assistant programs can upload text gathered from multiple sources (database, API calls) to the LLM and then return formatted documents based on that information. For example, you could send data retrieved via an API call to the LLM and ask it to summarize the data into a 1 page PDF suitable for an executive audience. The API calls would be something specific to your industry or use case like weather, exchange rates, financial data, logistical issues, legal changes, news stories and more. More info about this approach can be found here shortly (in development).
FAQ
Q. Can I use an existing dictionary? How about existing apps?
A. You can use your existing bootstrap application. Any maintainers or retrievals you wish to use with AI will need to be recompiled (but no need to overwrite the presentation layer.
Q. What version of dictionaries are supported?
A. While older dictionaries may work to various degrees, AI is supported in bootstrap templates only.
Q. Should I be concerned about data privacy?
A. You should always be concerned with data privacy! Using things like https ensure that data in transit is secure. Different AI Providers have different plans, tiers, and policies that you should review to ensure you understand if and how any data sent to it will be used. As far as trusting the AI provider, that is a decision that you and your organization must make. We do support a wide variety of AI providers should you prefer one over the other. Ultimately, which provider and plan you decide is best for your organization is up to you.
Q. I keep seeing LLM. What does that mean?
A. It stands for large language model. It is the driving process behind AI. AI providers typically offer different LLMs for your consideration. Some offer faster results with lower accuracy/lower cost, for instance. Within m-Power, you can select the LLM you wish to utilize, based on the AI provider you select.
Q. How accurate are AI results?
A. That is a tricky question to answer thoroughly but AI results can always be improved by better prompting of the AI. This typically means writing better prompts or providing more tool functions to better inform the LLM as to what you want. As the technology evolves, accuracy will continue to improve. Newer more powerful models typically provide greater accuracy.
Q. Are there additional costs for using AI features?
A. From mrc, no. This is considered a base feature of m-Power and is included in your m-Power license. However, depending on the AI company you choose, your usage, and the selected LLM, the costs do vary. LLM providers typically charge based on usage however unless your usage is very high the costs are nominal.
Q. I don’t know the first thing about AI. Where do I begin?
A. We understand that the prospect of setting up AI is a lot to take in. To help get you going on the right foot, mrc is offering companies between now and the end of 2026, a complimentary 4 hour consulting block to help you setup AI in your environment as well as assist you in building your first AI agent. Additional time is available for purchase if you wish to have continuing education on the topic.
